II.10 Report
on Organic Liquid Crystals
(Value 1 quiz grade due Thursday December 1)
A 7 page report.
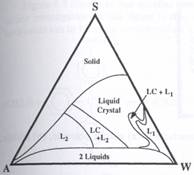
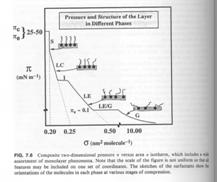
The following figures from Heimenz's book Colloid Science shows the presence of liquid crystalline phases in surfactant ternary phase diagrams and in surfactant monolayers.


You may have heard the terms "liquid crystal" in the context of watch, calculator and computer displays (a technology invented in the US at the University of Colorado under US NSF funding but now only produced in Asia). Ohio is a world leader in liquid crystal technology with an NSF center for liquid crystals at Kent State in northeastern Ohio and with expertise at Case Western in Cleveland. Although organic liquid crystals span a wide range of impact on science, from natural biological and medical importance to secondary oil recovery, materials scientists generally deal with four main aspects of liquid crystals,
1) low molecular-weight, electro-responsive, rigid molecules used for display devices,
2) main-chain liquid crystal polymers used for ultra high strength plastics including polyesters such as Kevlar made by Dupont and similar high-strength, ultra-oriented polymers developed in Dayton at the Wright Patterson Airforce Materials Directorate for stealth aerospace fuselages for example (the black stealth bomber fuselage is made using liquid crystalline polymers developed in Ohio),
3) Side chain liquid crystal polymers used for non-linear electro-optical components such as optical transistors in an optical computer (much faster than an electronic computer and with no generation of heat and very low power consumption).
4) Surfactant and block copolymer "micro-"phases.
-Define the terms lyotropic, thermotropic, disclination, orientation function, nematic, cholesteric, smectic.
-Explain the difference between a 3d crystal and a liquid crystal.
-Give chemical structure and synthetic path of two main-chain liquid-crystalline polymers including one developed by Dupont and developed by WPAFB in Dayton or under Airforce funding.
-Discuss generally the use of side-chain liquid-crystal polymers giving on example of a chemical structure and a synthetic scheme for a side chain liquid crystalline polymer (many were invented by Lenz at UMass).
-Mention generally how low molecular weight liquid crystals are used in display devices.
-Discuss ways to orient liquid crystals, for instance shear, electrical field, magnetic field, epitaxy, and others; and couple each of these with a commercial device, technology, or product such as a flak jacket or an i-pod video.
-Briefly mention how liquid crystals are involved in the surfactants shown in the figures above and in parallel biological membrane systems.